
The eSafety regulator in Australia has expressed concern over the misuse of the generative AI system Grok on social media platform X, following reports involving sexualised or exploitative content, particularly affecting children.
Although overall report numbers remain low, authorities in Australia have observed a recent increase over the past weeks.
The regulator confirmed that enforcement powers under the Online Safety Act remain available where content meets defined legal thresholds.
X and other services are subject to systemic obligations requiring the detection and removal of child sexual exploitation material, alongside broader industry codes and safety standards.
eSafety has formally requested further information from X regarding safeguards designed to prevent misuse of generative AI features and to ensure compliance with existing obligations.
Previous enforcement actions taken in 2025 against similar AI services resulted in their withdrawal from the Australian market.
Additional mandatory safety codes will take effect in March 2026, introducing new obligations for AI services to limit children’s exposure to sexually explicit, violent and self-harm-related material.
Authorities emphasised the importance of Safety by Design measures and continued international cooperation among online safety regulators.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!
Toy makers at the Consumer Electronics Show highlighted efforts to improve AI in playthings following troubling early reports of chatbots giving unsuitable responses to children’s questions.
A recent Public Interest Research Group report found that some AI toys, such as an AI-enabled teddy bear, produced inappropriate advice, prompting companies like FoloToy to update their models and suspend problematic products.
Among newer devices, Curio’s Grok toy, which refuses to answer questions deemed inappropriate and allows parental overrides, has earned independent safety certification. However, concerns remain about continuous listening and data privacy.
Experts advise parents to be cautious about toys that retain information over time or engage in ongoing interactions with young users.
Some manufacturers are positioning AI toys as educational tools, for example, language-learning companions with time-limited, guided chat interactions, and others have built in flags to alert parents when inappropriate content arises.
Despite these advances, critics argue that self-regulation is insufficient and call for clearer guardrails and possible regulation to protect children in AI-toy environments.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

The EU has agreed to open talks with the US on sharing sensitive traveller data. The discussions aim to preserve visa-free travel for European citizens.
The proposal is called ‘Enhanced Border Security Partnership‘, and it could allow transfers of biometric data and other sensitive personal information. Legal experts warn that unclear limits may widen access beyond travellers alone.
EU governments have authorised the European Commission to negotiate a shared framework. Member states would later settle details through bilateral agreements with Washington.
Academics and privacy advocates are calling for stronger safeguards and transparency. EU officials insist data protection limits will form part of any final agreement.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

A US teenager targeted by explicit deepfake images has helped create a new training course. The programme aims to support students, parents and school staff facing online abuse.
The course explains how AI tools are used to create sexualised fake images. It also outlines legal rights, reporting steps and available victim support resources.
Research shows deepfake abuse is spreading among teenagers, despite stronger laws. One in eight US teens know someone targeted by non-consensual fake images.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

Google is expanding shopping features inside its Gemini chatbot through partnerships with Walmart and other retailers. Users will be able to browse and buy products without leaving the chat interface.
An instant checkout function allows purchases through linked accounts and selected payment providers. Walmart customers can receive personalised recommendations based on previous shopping activity.
The move was announced at the latest National Retail Federation convention in New York. Tech groups are racing to turn AI assistants into end-to-end retail tools.
Google said the service will launch first in the US before international expansion. Payments initially rely on Google-linked cards, with PayPal support planned.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

Canopy Healthcare, one of New Zealand’s largest private medical oncology providers, has disclosed a data breach affecting patient and staff information, six months after the incident occurred.
The company said an unauthorised party accessed part of its administration systems on 18 July 2025, copying a ‘small’ amount of data. Affected information may include patient records, passport details, and some bank account numbers.
Canopy said it remains unclear exactly which individuals were impacted and what data was taken, adding that no evidence has emerged of the information being shared or published online.
Patients began receiving notifications in December 2025, prompting criticism over the delay. One affected patient said they were unhappy to learn about the breach months after it happened.
The New Zealand company said it notified police and the Privacy Commissioner at the time, secured a High Court injunction to prevent misuse of the data, and confirmed that its medical services continue to operate normally.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech, and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!
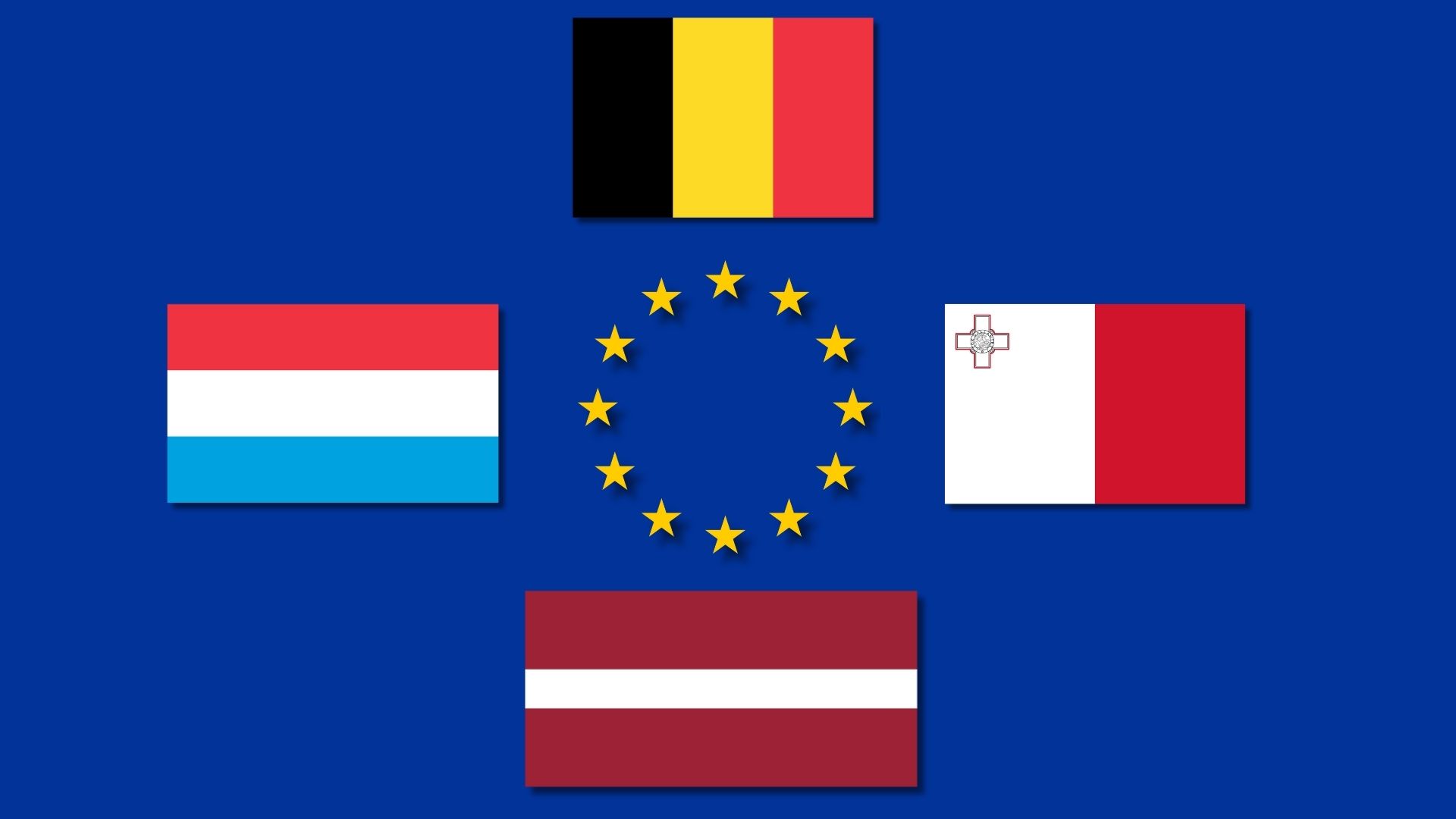

Luxembourg has hosted its largest national cyber defence exercise, Cyber Fortress, bringing together military and civilian specialists to practise responding to real-time cyberattacks on digital systems.
Since its launch in 2021, Cyber Fortress has evolved beyond a purely technical drill. The exercise now includes a realistic fictional scenario supported by media injections, creating a more immersive and practical training environment for participants.
This year’s edition expanded its international reach, with teams joining from Belgium, Latvia, Malta and the EU Cyber Rapid Response Teams. Around 100 participants also took part from a parallel site in Latvia, working alongside Luxembourg-based teams.
The exercise focuses on interoperability during cyber crises. Participants respond to multiple simulated attacks while protecting critical services, including systems linked to drone operations and other sensitive infrastructure.
Cyber Fortress now covers technical, procedural and management aspects of cyber defence. A new emphasis on disinformation, deepfakes and fake news reflects the growing importance of information warfare.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech, and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer is consulting Canada and Australia on a coordinated response to concerns surrounding social media platform X, after its AI assistant Grok was used to generate sexualised deepfake images of women and children.
The discussions focus on shared regulatory approaches rather than immediate bans.
X acknowledged weaknesses in its AI safeguards and limited image generation to paying users. Lawmakers in several countries have stated that further regulatory scrutiny may be required, while Canada has clarified that no prohibition is currently under consideration, despite concerns over platform responsibility.
In the UK, media regulator Ofcom is examining potential breaches of online safety obligations. Technology secretary Liz Kendall confirmed that enforcement mechanisms remain available if legal requirements are not met.
Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese also raised broader concerns about social responsibility in the use of generative AI.
X owner Elon Musk rejected accusations of non-compliance, describing potential restrictions as censorship and suppression of free speech.
European authorities requested the preservation of internal records for possible investigations, while Indonesia and Malaysia have already blocked access to the platform.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

Google removed some AI health summaries after a Guardian investigation found they gave misleading and potentially dangerous information. The AI Overviews contained inaccurate liver test data, potentially leading patients to believe they were healthy falsely.
Experts have criticised AI Overviews for oversimplifying complex medical topics, ignoring essential factors such as age, sex, and ethnicity. Charities have warned that misleading AI content could deter people from seeking medical care and erode trust in online health information.
Google removed AI Overviews for some queries, but concerns remain over cancer and mental health summaries that may still be inaccurate or unsafe. Professionals emphasise that AI tools must direct users to reliable sources and advise seeking expert medical input.
The company stated it is reviewing flagged examples and making broad improvements, but experts insist that more comprehensive oversight is needed to prevent AI from dispensing harmful health misinformation.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!

India’s Financial Intelligence Unit has tightened crypto compliance, requiring live identity checks, location verification, and stronger Client Due Diligence. The measures aim to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and misuse of digital asset services.
Crypto platforms must now collect multiple identifiers from users, including IP addresses, device IDs, wallet addresses, transaction hashes, and timestamps.
Verification also requires users to provide a Permanent Account Number and a secondary ID, such as a passport, Aadhaar, or voter ID, alongside OTP confirmation for email and phone numbers.
Bank accounts must be validated via a penny-drop mechanism to confirm ownership and operational status.
Enhanced due diligence will apply to high-risk transactions and relationships, particularly those involving users from designated high-risk jurisdictions and tax havens. Platforms must monitor red flags and apply extra scrutiny to comply with the new guidelines.
Industry experts have welcomed the updated rules, describing them as a positive step for India’s crypto ecosystem. The measures are viewed as enhancing transparency, protecting users, and aligning the sector with global anti-money laundering standards.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!










