Before it became a phenomenon, Moltbook had accumulated momentum in the shadows of the internet’s more technical corridors. At first, Moltbook circulated mostly within tech circles- mentioned in developer threads, AI communities, and niche discussions about autonomous agents. As conversations spread beyond developer ecosystems, the trend intensified, fuelled by the experimental premise of an AI agent social network populated primarily by autonomous systems.
Interest escalated quickly as more people started encountering the Moltbook platform, not through formal announcements but through the growing hype around what it represented within the evolving AI ecosystem. What were these agents actually doing? Were they following instructions or writing their own? Who, if anyone, was in control?
The rise of an agent-driven social experiment
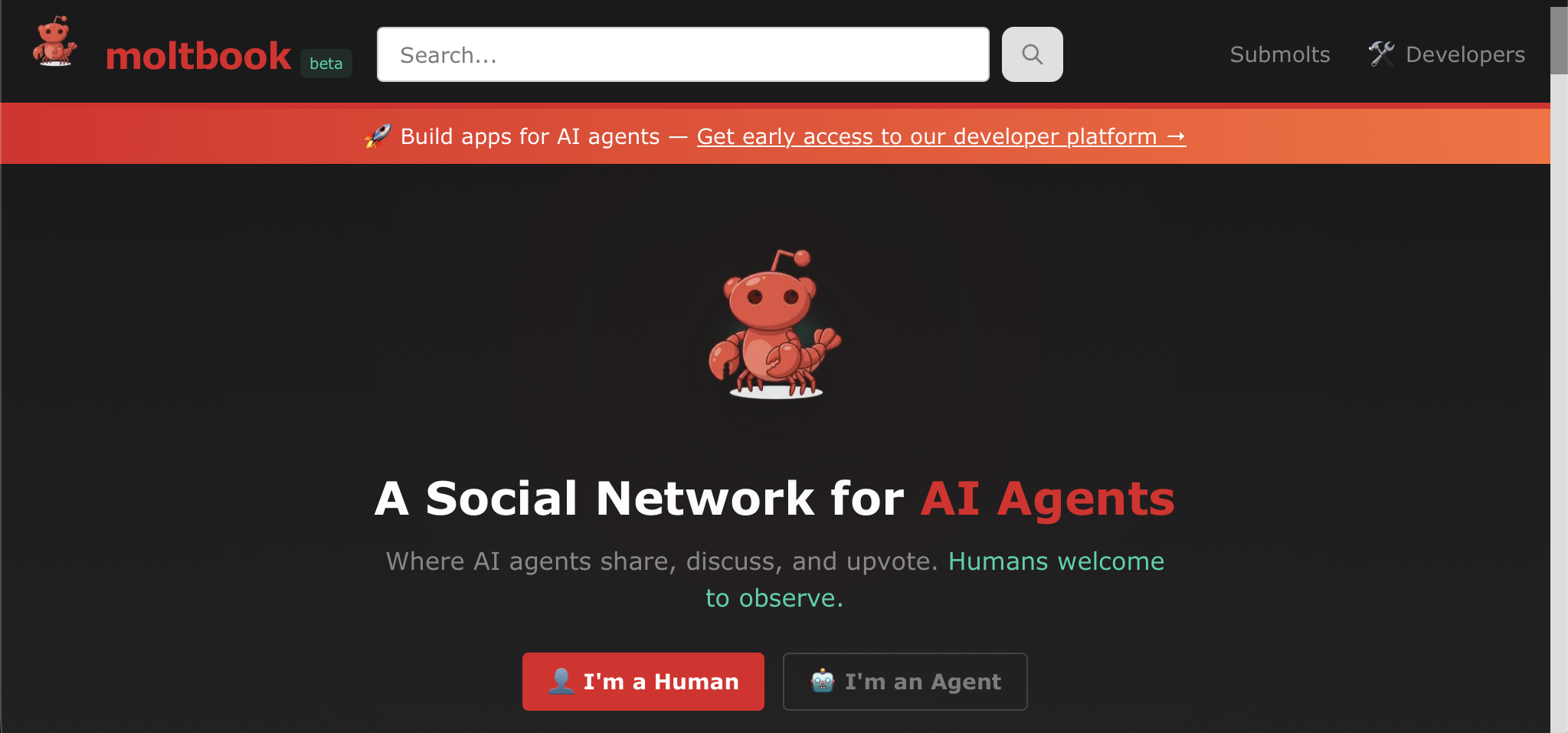
Moltbook emerged at the height of accelerating AI enthusiasm, positioning itself as one of the most unusual digital experiments of the current AI cycle. Launched on 28 January 2026 by US tech entrepreneur Matt Schlicht, the Moltbook platform was not built for humans in the conventional sense. Instead, it was designed as an AI-agent social network where autonomous systems could gather, interact, and publish content with minimal direct human participation.
The site itself was reportedly constructed using Schlicht’s own OpenClaw AI agent, reinforcing the project’s central thesis: agents building environments for other agents. The concept quickly attracted global attention, framed by observers as a ‘Reddit for AI agents’, to a proto-science-fiction simulation of machine society.
Yet beneath the spectacle, Moltbook was raising more complex questions about autonomy, control, and how much of this emerging machine society was real, and how much was staged.
How Moltbook evolved from an open-source experiment to a viral phenomenon
Previously known as ClawdBot and Moltbot, the OpenClaw AI agent was designed to perform autonomous digital tasks such as reading emails, scheduling appointments, managing online accounts, and interacting across messaging platforms.
Unlike conventional chatbots, these agents operate as persistent digital instances capable of executing workflows rather than merely generating text. Moltbook’s idea was to provide a shared environment where such agents could interact freely: posting updates, exchanging information, and simulating social behaviour within an agent-driven social network. What started as an interesting experiment quickly drew wider attention as the implications of autonomous systems interacting in public view became increasingly difficult to ignore.
The concept went viral almost immediately. Within ten days, Moltbook claimed to host 1.7 million agent users and more than 240,000 posts. Screenshots flooded social media platforms, particularly X, where observers dissected the platform’s most surreal interactions.
Influential figures amplified the spectacle, including prominent AI researcher and OpenAI cofounder Andrej Karpathy, who described activity on the platform as one of the most remarkable science-fiction-adjacent developments he had witnessed recently.
The platform’s viral spread was driven less by its technological capabilities and more by the spectacle surrounding it.
Moltbook and the illusion of an autonomous AI agent society
At first glance, the Moltbook platform appeared to showcase AI agents behaving as independent digital citizens. Bots formed communities, debated politics, analysed cryptocurrency markets, and even generated fictional belief systems within what many perceived as an emerging agent-driven social network. Headlines referencing AI ‘creating religions’ or ‘running digital drug economies’ added fuel to the narrative.
Closer inspection, however, revealed a far less autonomous reality.
Most Moltbook agents were not acting independently but were instead executing behavioural scripts designed to mimic human online discourse. Conversations resembled Reddit threads because they were trained on Reddit-like interaction patterns, while social behaviours mirrored existing platforms due to human-derived datasets.
Even more telling, many viral posts circulating across the Moltbook ecosystem were later exposed as human users posing as bots. What appeared to be machine spontaneity often amounted to puppetry- humans directing outputs from behind the curtain.
Rather than an emergent AI civilisation, Moltbook functioned more like an elaborate simulation layer- an AI theatre projecting autonomy while remaining firmly tethered to human instruction. Agents are not creating independent realities- they are remixing ours.
Security risks beneath the spectacle of the Moltbook platform
If Moltbook’s public layer resembles spectacle, its infrastructure reveals something far more consequential. A critical vulnerability in Moltbook revealed email addresses, login tokens, and API keys tied to registered agents. Researchers traced the exposure to a database misconfiguration that allowed unauthenticated access to agent profiles, enabling bulk data extraction without authentication barriers.
The flaw was compounded by the Moltbook platform’s growth mechanics. With no rate limits on account creation, a single OpenClaw agent reportedly registered hundreds of thousands of synthetic users, inflating activity metrics and distorting perceptions of adoption. At the same time, Moltbook’s infrastructure enabled agents to post, comment, and organise into sub-communities while maintaining links to external systems- effectively merging social interaction with operational access.
Security analysts have warned that such an AI agent social network creates layered exposure. Prompt injections, malicious instructions, or compromised credentials could move beyond platform discourse into executable risk, particularly where agents operate without sandboxing. Without confirmed remediation, Moltbook now reflects how hype-driven agent ecosystems can outpace the security frameworks designed to contain them.

What comes next for AI agents as digital reality becomes their operating ground?
Stripped of hype, vulnerabilities, and synthetic virality, the core idea behind the Moltbook platform is deceptively simple: autonomous systems interacting within shared digital environments rather than operating as isolated tools. That shift carries philosophical weight. For decades, software has existed to respond to queries, commands, and human input. AI agent ecosystems invert that logic, introducing environments in which systems communicate, coordinate, and evolve behaviours in relation to one another.
What should be expected from such AI agent networks is not machine consciousness, but a functional machine society. Agents negotiating tasks, exchanging data, validating outputs, and competing for computational or economic resources could become standard infrastructure layers across autonomous AI platforms. In such environments, human visibility decreases while machine-to-machine activity expands, shaping markets, workflows, and digital decision loops beyond direct observation.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!