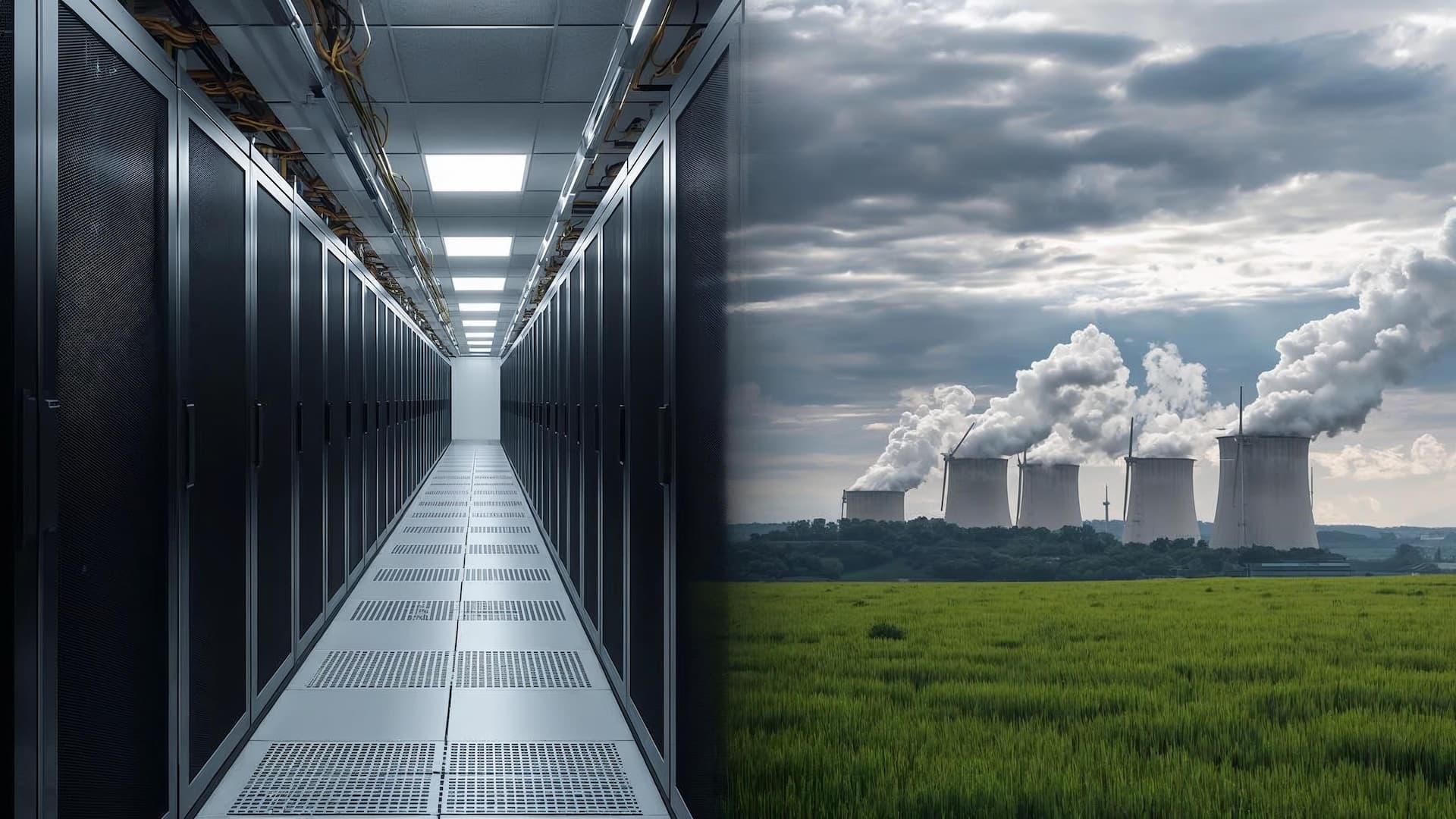
Rising AI-driven electricity demand is straining power grids and renewing focus on nuclear energy as a stable, low-carbon solution. Data centres powering AI systems already consume electricity at the scale of small cities, and demand is accelerating rapidly.
Global electricity consumption could rise by more than 10,000 terawatt-hours by 2035, largely driven by AI workloads. In advanced economies, data centres are expected to drive over a fifth of electricity-demand growth by 2030, outpacing many traditional industries.
Nuclear energy is increasingly positioned as a reliable backbone for this expansion, offering continuous power, high energy density, and grid stability.
Governments, technology firms, and nuclear operators are advancing new reactor projects, while long-term power agreements between tech companies and nuclear plants are becoming more common.
Alongside large reactors, interest is growing in small modular reactors designed for faster deployment near data centres. Supporters say these systems could ease grid bottlenecks and deliver dedicated power for AI, strengthening nuclear energy’s role in the digital economy.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!