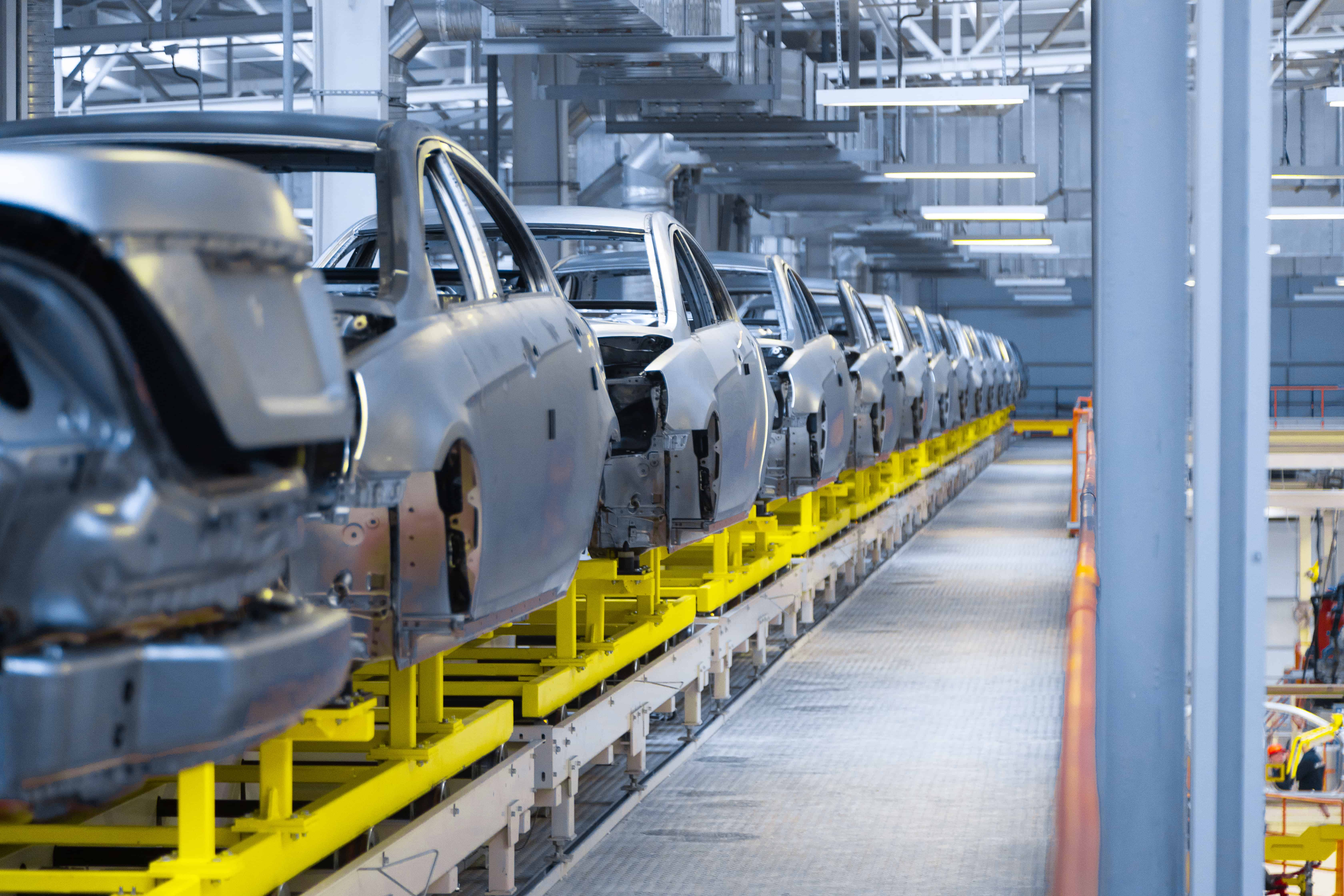
Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) has confirmed that its production halt will continue until at least Wednesday, 24 September, as it works to recover from a major cyberattack that disrupted its IT systems and paralysed production at the end of August.
JLR stated that the extension was necessary because forensic investigations were ongoing and the controlled restart of operations was taking longer than anticipated. The company stressed that it was prioritising a safe and stable restart and pledged to keep staff, suppliers, and partners regularly updated.
Reports suggest recovery could take weeks, impacting production and sales channels for an extended period. Approximately 33,000 employees remain at home as factory and sales processes are not fully operational, resulting in estimated losses of £1 billion in revenue and £70 million in profits.
The shutdown also poses risks to the wider UK economy, as JLR represents roughly four percent of British exports. The incident has renewed calls for the Cyber Security and Resilience Bill, which aims to strengthen defenses against digital threats to critical industries.
No official attribution has been made, but a group calling itself Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters has claimed responsibility. The group claims to have deployed ransomware and published screenshots of JLR’s internal SAP system, linking itself to extortion groups, including Scattered Spider, Lapsus$, and ShinyHunters.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech, and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!