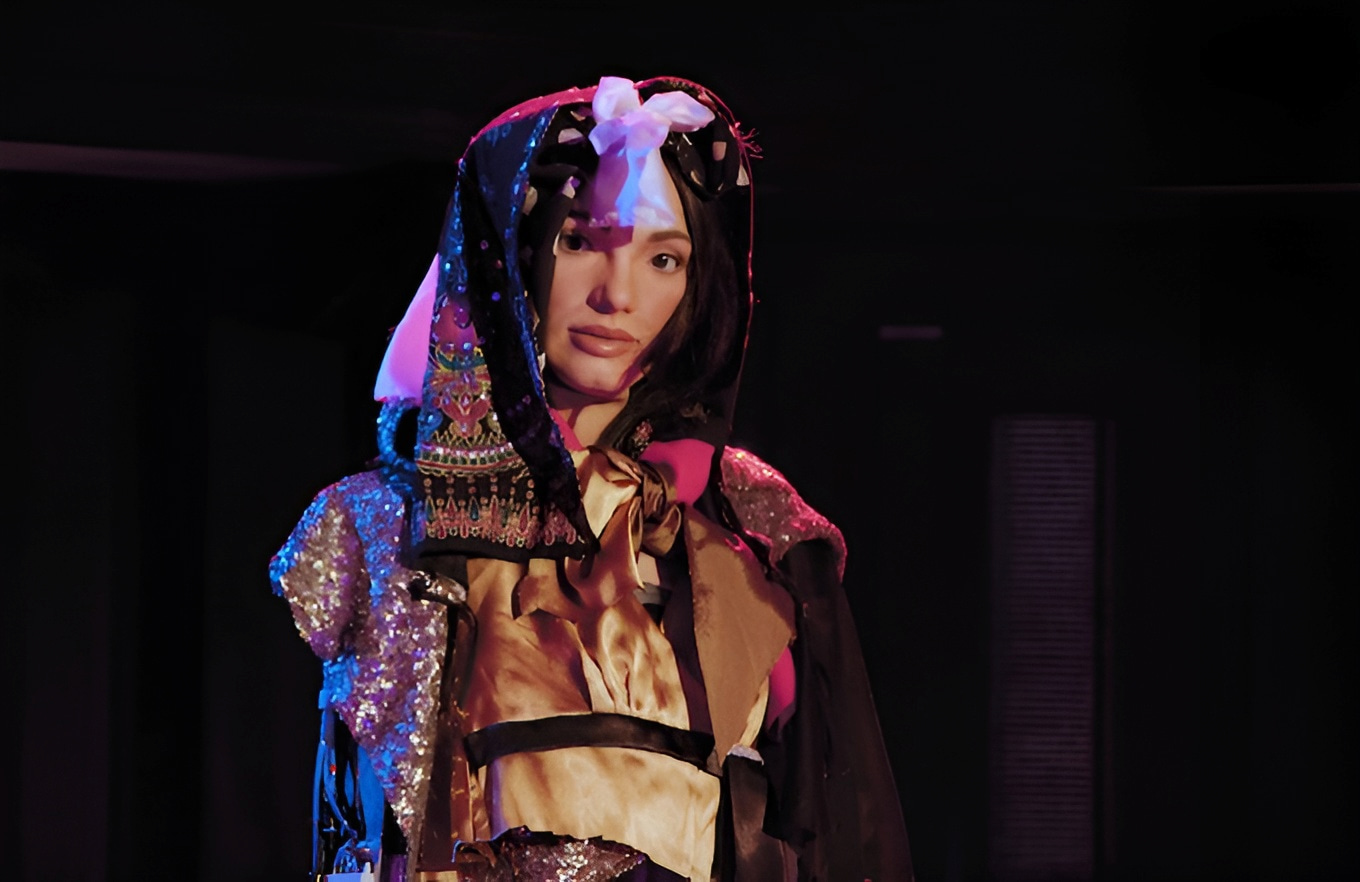
The world’s first ultra-realistic robot artist, Ai-Da, has been prompting profound questions about human-robot interactions, according to her creator.
Designed in Oxford by Aidan Meller, a modern and contemporary art specialist, and built in the UK by Engineered Arts, Ai-Da is a humanoid robot specifically engineered for artistic creation. She recently unveiled a portrait of King Charles III, adding to her notable portfolio.
Aidan Meller, Ai-Da’s creator, stated that working with the robot has evoked ‘lots of questions about our relationship with ourselves.’ He highlighted how Ai-Da’s artwork ‘drills into some of our time’s biggest concerns and thoughts.’
Ai-Da uses cameras in her eyes to capture images, which are then processed by AI algorithms and converted into real-time coordinates for her robotic arm, enabling her to paint and draw.
Mr Meller explained, ‘You can meet her, talk to her using her language model, and she can then paint and draw you from sight.’
He also observed that people’s preconceptions about robots are often outdated: ‘It’s not until you look a robot in the eye and they say your name that the reality of this new sci-fi world that we are now in takes hold.’
Ai-Da’s contributions to the art world continue to grow. She had produced and showcased her work at the AI for Good Global Summit 2024 in Geneva, Switzerland, an event under the auspices of the UN. That same year, her triptych of Enigma code-breaker Alan Turing sold for over £1 million at auction.
Her focus this year shifted to King Charles III, chosen because, as Mr Meller noted, ‘With extraordinary strides that are taking place in technology and again, always questioning our relationship to the environment, we felt that King Charles was an excellent subject.’
Buckingham Palace authorised the display of Ai-Da’s portrait of the King, despite the robot not meeting him. Ai-Da, connected to the internet, uses extensive data to inform her choice of subjects, with Mr Meller revealing, ‘Uncannily, and rather nerve-rackingly, we just ask her.’
The conversations generated inform the artwork. Ai-Da also painted a portrait of King Charles’s mother, Queen Elizabeth II, in 2023. Mr Meller shared that the most significant realisation from six years of working with Ai-Da was ‘not so much about how human she is but actually how robotic we are.’
He concluded, ‘We hope Ai-Da’s artwork can be a provocation for that discussion.’
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!