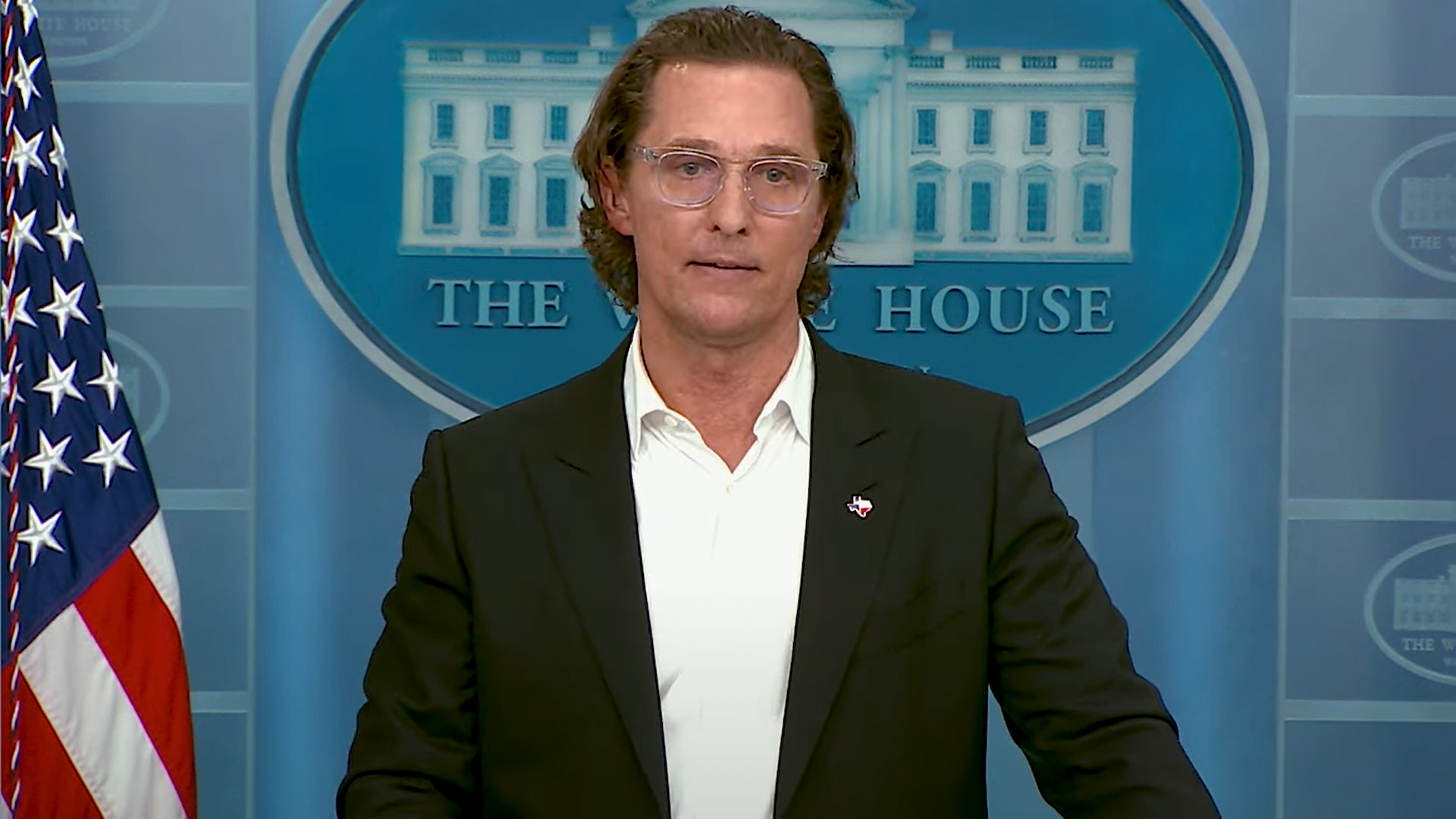
Oscar-winning actor Matthew McConaughey has trademarked his image and voice to protect them from unauthorised use by AI platforms. His lawyers say the move is intended to safeguard consent and attribution in an evolving digital environment.
Several clips, including his well-known catchphrase from Dazed and Confused, have been registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office. Legal experts say it is the first time an actor has used trademark law to address potential AI misuse of their likeness.
McConaughey’s legal team said there is no evidence of his image being manipulated by AI so far. The trademarks are intended to act as a preventative measure against unauthorised copying or commercial use.
The actor said he wants to ensure any future use of his voice or appearance is approved. Lawyers also said the approach could help capture value created through licensed AI applications.
Concerns over deepfakes and synthetic media are growing across the entertainment industry. Other celebrities have faced unauthorised AI-generated content, prompting calls for stronger legal protections.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech, and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!