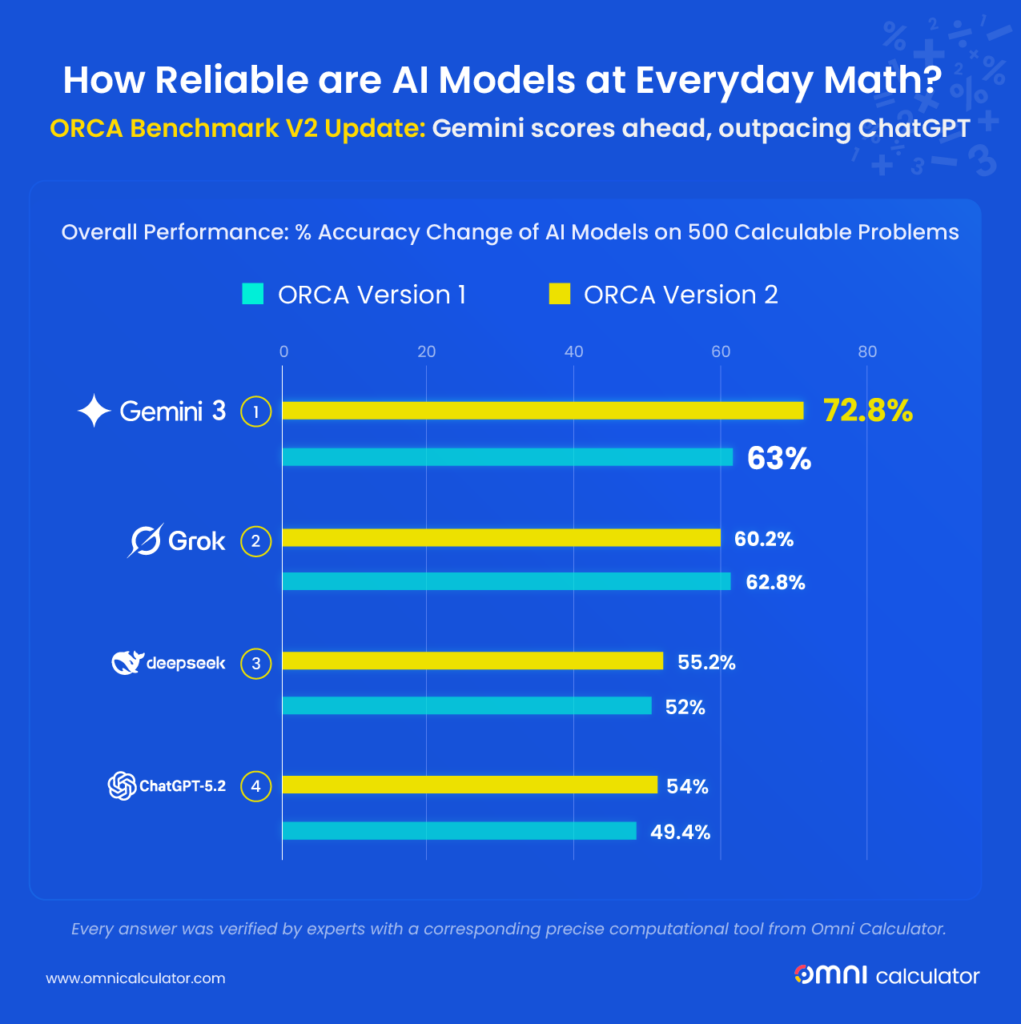
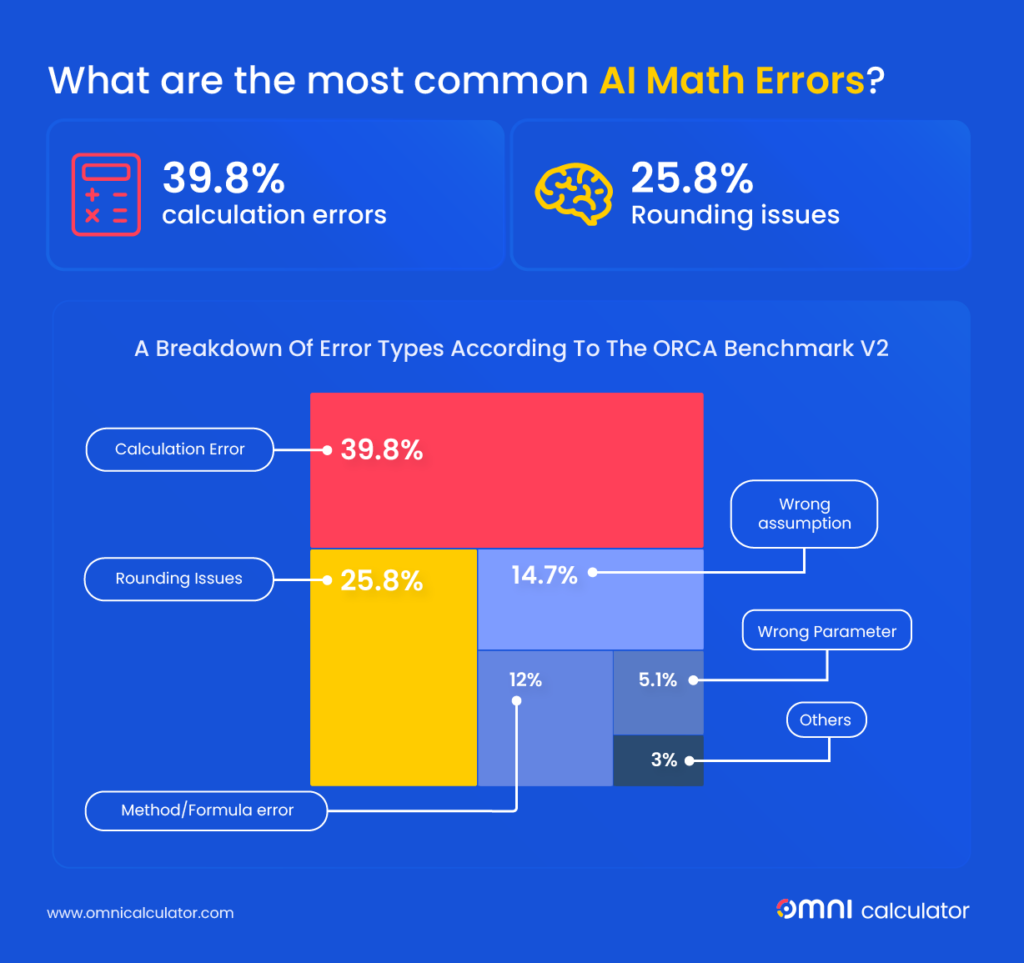
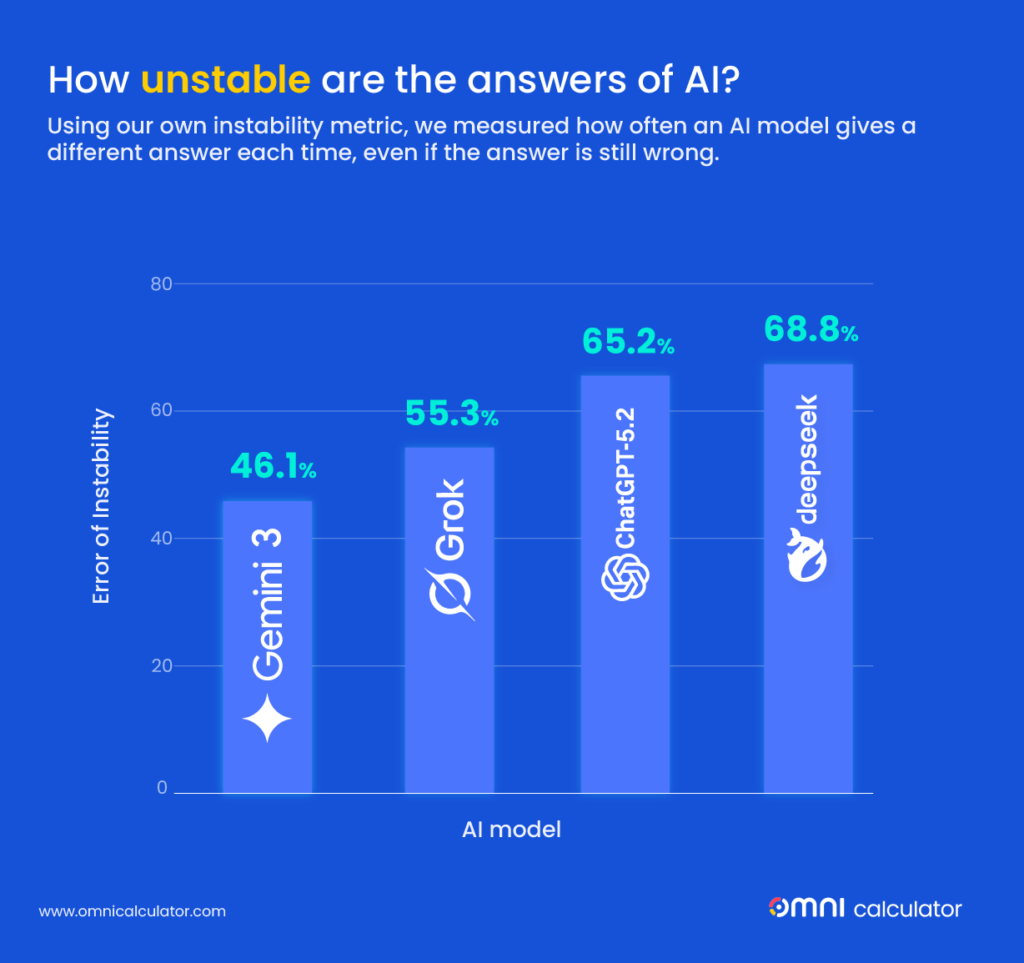
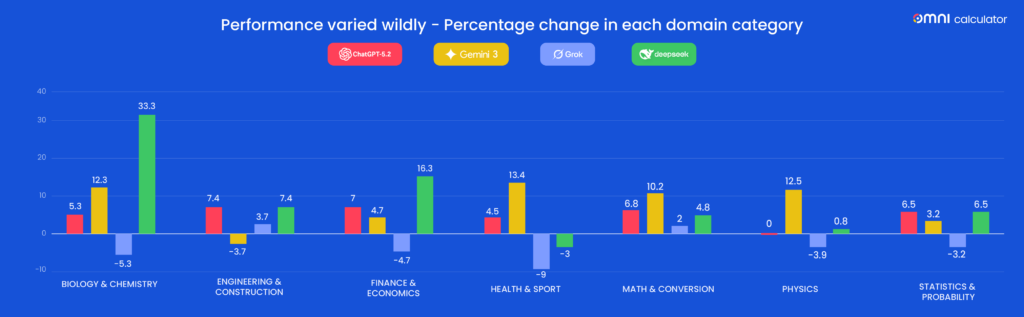
AI systems rely heavily on human labour to train and improve algorithms. Images and videos collected by AI-powered devices are often reviewed and labelled by human annotators so that systems can better recognise objects, environments, and context.
This work is frequently outsourced to data annotation companies such as Sama, which provides training data services for large technology firms, including Meta Platforms. Many of these tasks are carried out by contract workers in Nairobi, Kenya, where employees review large volumes of visual data under strict confidentiality agreements.
Recent investigations have raised concerns about privacy and data governance linked to AI wearables such as the Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses, developed in partnership with EssilorLuxottica. Some device features rely on cloud processing, meaning that captured images and voice inputs may be transmitted and analysed remotely.
Workers involved in the annotation process report regularly encountering sensitive material. Footage can include scenes recorded inside private homes, bedrooms, or bathrooms, as well as images that unintentionally reveal personal or financial information.
These practices raise broader questions about transparency and cross-border data transfers, particularly when data originating in Europe or the United States is processed in other countries. They also highlight the often-hidden human role behind AI systems that are frequently presented as fully automated technologies.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!