EU sets privacy defaults to shield minors
Policymakers are stepping up efforts to make the digital world safer for children by combining stricter rules with new technological tools.
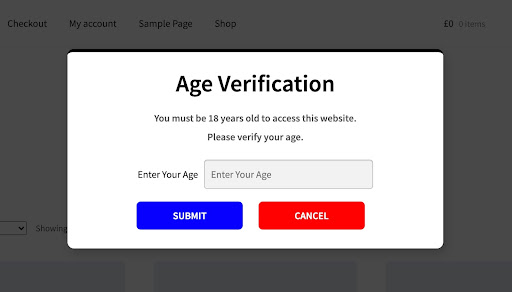
The European Commission has published new guidelines to help online platforms strengthen child protection, alongside unveiling a prototype age verification app under the Digital Services Act (DSA). The guidance addresses a broad range of risks to minors, from harmful content and addictive design features to unwanted contact and cyberbullying, urging platforms to set children’s accounts to the highest privacy level by default and limit risky functions like geo-location.
Officials stressed that the rules apply to platforms of all sizes and are based on a risk-based approach. Websites dealing with alcohol, drugs, pornography, or gambling were labelled ‘high-risk’ and must adopt the strictest verification methods. While parental controls remain optional, the Commission emphasised that any age assurance system should be accurate, reliable, non-intrusive, and non-discriminatory.
Alongside the guidelines, the Commission introduced a prototype age verification app, which it calls a ‘gold standard’ for online age checks. Released as open-source code, the software is designed to confirm whether a user is above 18, but can be adapted for other age thresholds.
The prototype will be tested in Denmark, France, Greece, Italy, and Spain over the coming months, with flexibility for countries to integrate it into national systems or offer it as a standalone tool. Both the guidelines and the app will be reviewed in 12 months, as the EU continues refining its approach to child safety online.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!
